Helm for the Second Time – Versioning and Rollbacks for Your Application
We describe how to perform an update and rollback in Helm, how to flexibly overwrite values, and discover what templates are and how they work.
 Author:
Author:The starting point for the process of strategic analysis in the area of IT technology should be the goals and general strategy of the company, expressed in answers to the following questions[1]:
After determining the anticipated/desired situation on the market, it is necessary to determine the technological needs (including in the IT area), which should be the purpose of a technological audit of the company. Generally, an audit is used to assess, carried out by a competent and independent audit team, whether the entity subjected to the assessment meets certain patterns and standards, expressed in previously codified requirements. A technological audit should include[2]:
The subject of the technological potential audit should be individual IT technologies as well as groups of related IT technologies. The assessment should be based on the current degree of utilization of the capabilities of the IT technologies (including, m.in. technological devices, server rooms, external IT services), with a focus on those IT technologies that directly affect the level of competitiveness of existing products, including quality, costs, execution time, consumption of energy, materials, environmental pollution, etc. Usually, the possibilities of IT technology at the company’s disposal are not fully exploited. The identified gap can be mitigated through a variety of improvement measures, including improving the use of IT technology (through organizational changes) or modernizing it (which requires investment).
The assessment of the technological potential of a company’s IT is also related to determining the extent to which it has mastered the ability to use IT technology. It is expressed by the competitive position of the entity, which can be:
The so-called portfolio methods can be helpful in the analysis and assessment of technological potential. They consist in the analysis of a set (portfolio, set) of IT technologies used or required for the production of specific products. One of the leading methods of portfolio technology analysis is the A.D. Little model (Figure 1). Individual IT technologies are presented in the form of circles, arranged in a matrix, in a position corresponding to the technology assessment on the following scales:
The third criterion is the size of the resources involved in a given IT technology, symbolized by the size of the diameter of the circle. In the example presented in Figure 1, the IT technology portfolio (and thus the company’s competitive position in the field of technology) can be described as positive. This is evidenced by its favourable position in key technologies. The low commitment to future-oriented technologies may be worrying. Hypothetical decisions, shown in Figure 1, serve to maintain or strengthen the company’s technological potential in the IT area, thanks to which the competitive position in various market segments will be strengthened or maintained.
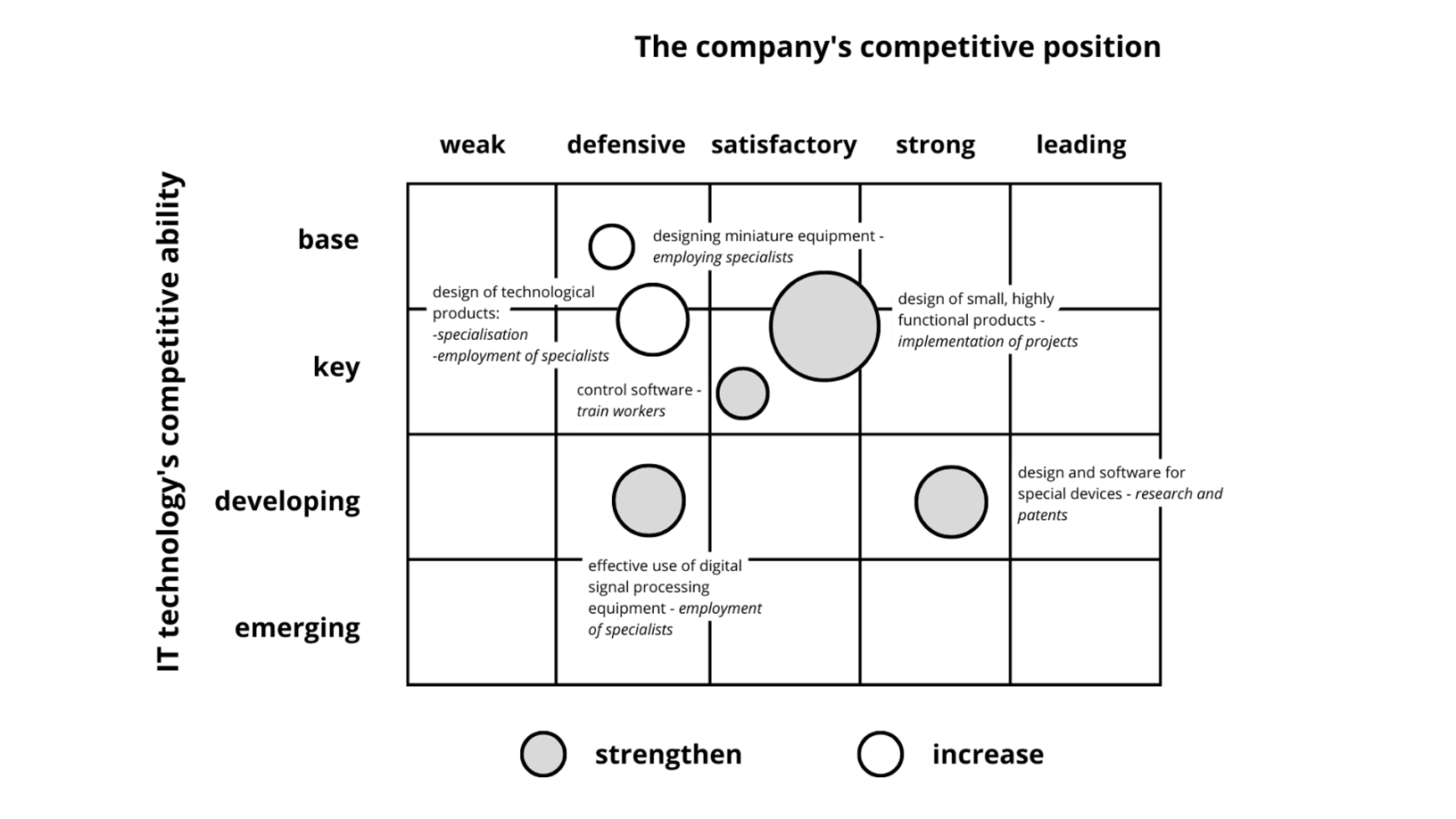
Figure 1. Example of the A.D.Little model of portfolio analysis of IT technologies used in the enterprise
Source: Based on K. Santarek (ed.), Technology transfer from academia to business. Creating Technology Transfer Mechanisms, PARP, Warsaw, September 2008, p. 25.
The audit of the applied procedures goes far beyond technological issues and covers the areas discussed below (after: P. Głodek, M. Gołębiowski):
The result of the review of IT technology resources and technological potential, as well as the identification and evaluation of the procedures used, should be the determination of the needs in terms of the necessary IT technologies and knowledge, as well as the ways to acquire them and strengthen the technological position of the enterprise. For this purpose, you can use internal, external and combined sources, discussed by us in our previous article. Among the channels of acquiring IT technologies that can be used, we can m.in mention:

The choice of the source and method of obtaining technologies depends on their availability on the market, their importance to the company and its capabilities. Examples of ways of acquiring technologies of various importance for the competitiveness of the company’s products are presented in the Figure 2.
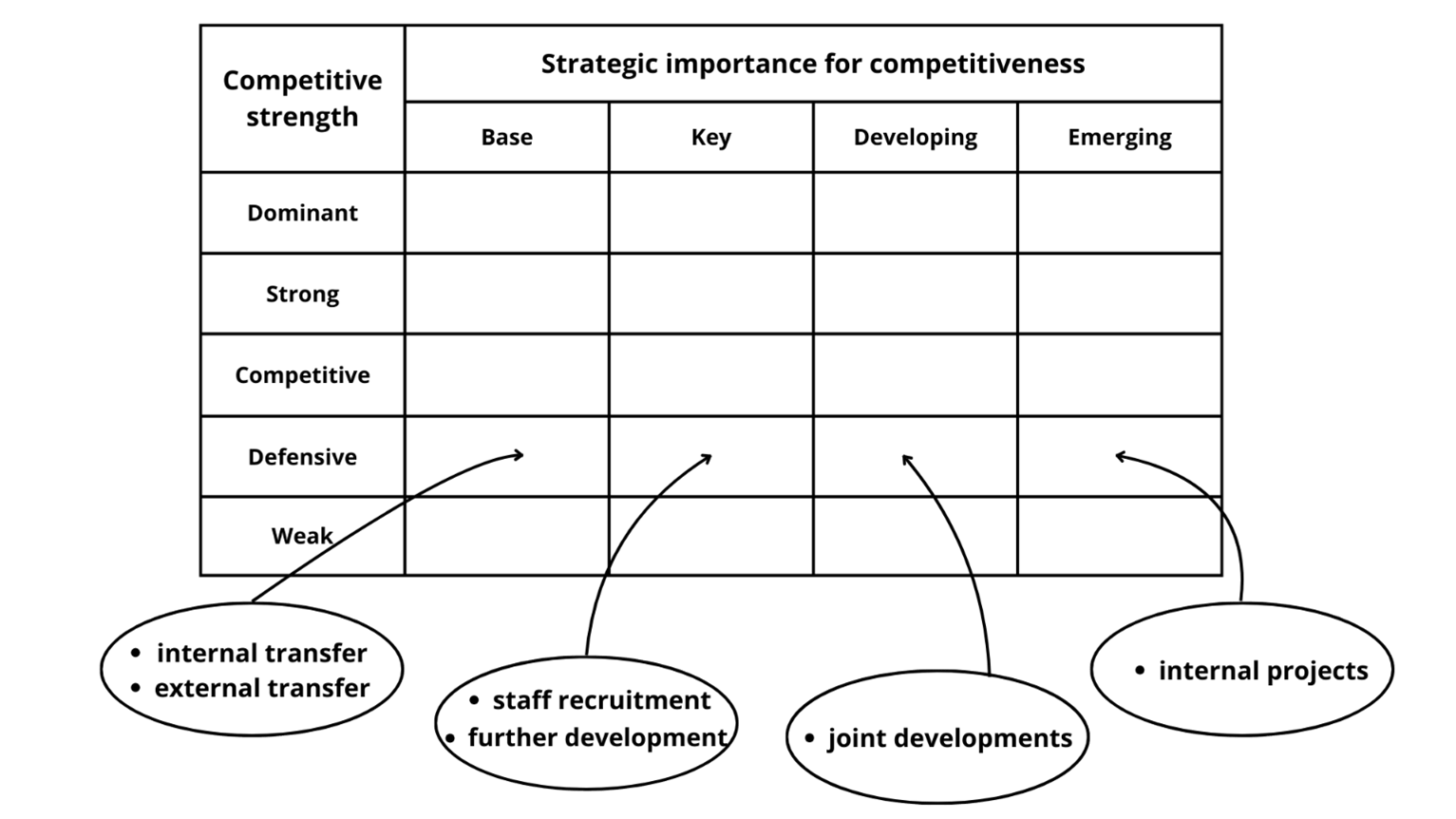
Figure 2. Exemplary channels of IT technology acquisition by the company
Author’s own elaboration based on: K. Santarek (ed.), Transfer of technology from universities to business. Creating Technology Transfer Mechanisms, PARP, Warsaw, September 2008, p. 27.
[1] K. Santarek (ed.), Transfer of technology from academia to business. Creating Technology Transfer Mechanisms, PARP, Warsaw, September 2008, p. 19.
[2] Prepared on the basis of K. Santarek (ed.), Transfer of technology from universities to business. Creating mechanisms for technology transfer, PARP, Warsaw, September 2008, pp. 19-27; P. Głodek, M. Gołębiowski, Technology transfer in small … Op. Cit. pp. 22-23.

Helm for the Second Time – Versioning and Rollbacks for Your Application
We describe how to perform an update and rollback in Helm, how to flexibly overwrite values, and discover what templates are and how they work.
AdministrationInnovation

Helm – How to Simplify Kubernetes Management?
It's worth knowing! What is Helm, how to use it, and how does it make using a Kubernetes cluster easier?
AdministrationInnovation

INNOKREA at Greentech Festival 2025® – how we won the green heart of Berlin
What does the future hold for green technologies, and how does our platform fit into the concept of recommerce? We report on our participation in the Greentech Festival in Berlin – see what we brought back from this inspiring event!
EventsGreen IT